What is ASSETS ?
Assets are a vital investment for any organization, playing a crucial role in supporting operations, generating revenue, enabling business activities, and facilitating projects, research, and educational initiatives. They are essential for carrying out the day-to-day functions of many organizations.
Types of Assets
Tangible Assets
Tangible Assets are Physical items that have value and can be used by businesses or individuals. Examples include equipment, machinery, computers, instruments Office furniture, etc
Intangible Assets
Intangible Assets are non-physical assets that gain value over time. These include Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) such as patents, trademarks, and copyrights.
Assets of an Institution or Organization
An institution or organization gradually invests in a wide range of assets to strengthen its operations, infrastructure, education, research, and development efforts. These assets may include buildings, equipment, software, vehicles, and other valuable resources. Over time, they represent a substantial share of the institution’s financial investment. Proper management of these assets is essential for ensuring sustainability, achieving long-term goals, and maximizing overall institutional performance and impact
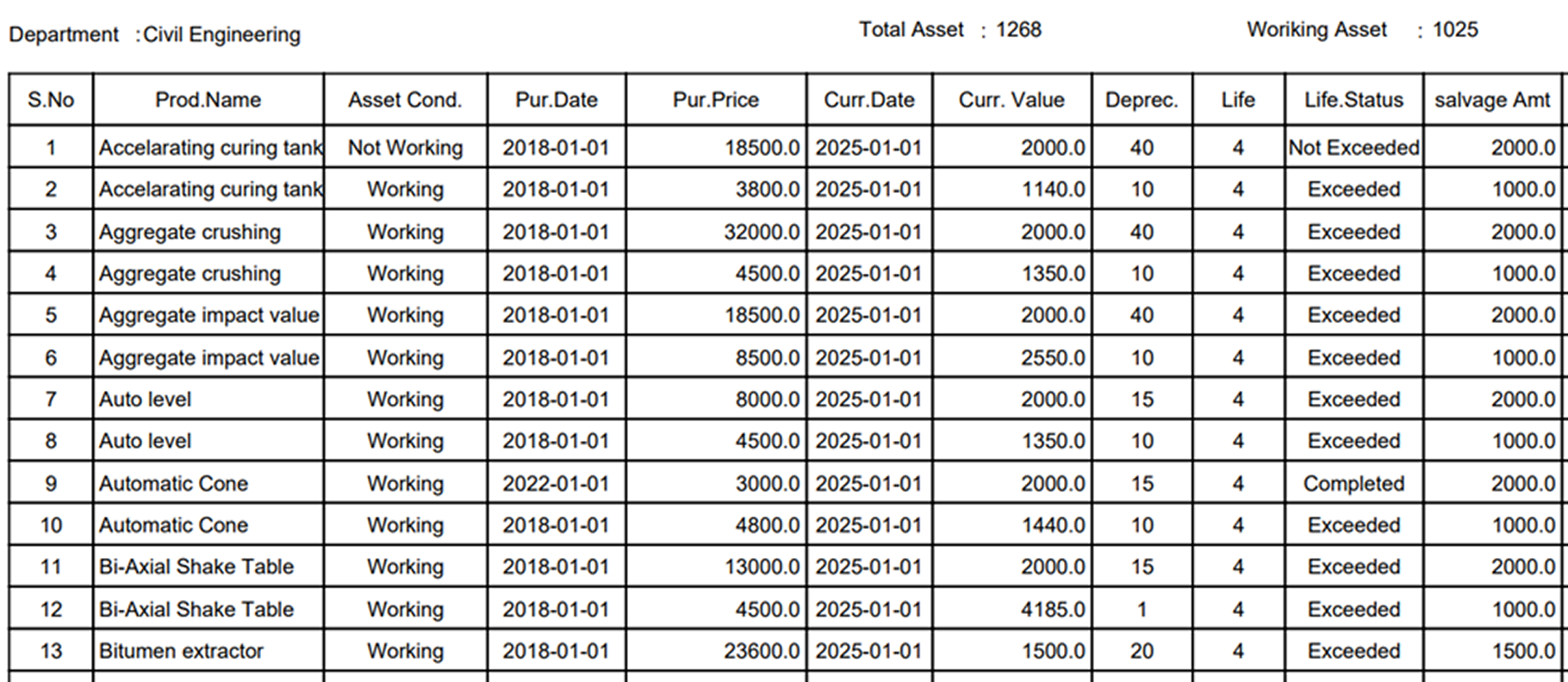
Asset Auditing
Asset auditing involves systematically assessing the condition and status of assets from the date of purchase. This process uses several parameters, including asset value, age, physical condition, depreciation, lifecycle stage, current market value, salvage value, and operational efficiency. Regular auditing helps ensure accurate asset tracking, optimal utilization, and informed decision-making regarding maintenance, replacement, or disposal and future purchase
Why do we need an Asset Management System?
Many institutions often lack a well-structured system or proper inventory management process to track and monitor assets from the time of acquisition. Without accurate records, it becomes challenging to determine the current location, usage status, or physical condition of each asset. This lack of visibility can lead to inefficiencies, misplacement, underutilization, or even loss of valuable resources, ultimately affecting operational effectiveness and informed decision-making
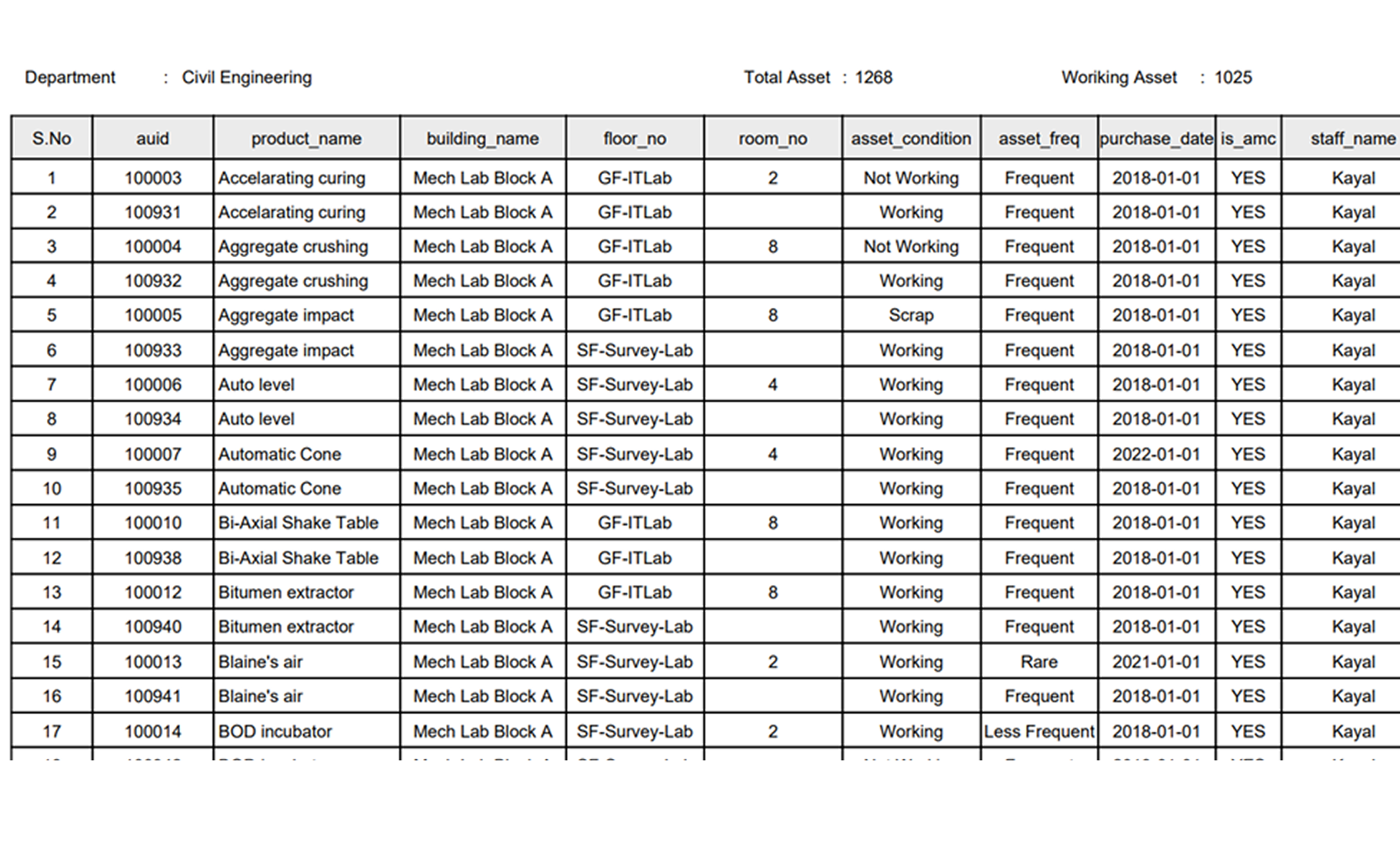
Asset Inventory And Auditing System
The Asset Inventory and Auditing Management System (AIAMS) empowers institutions and organizations to effectively monitor the real-time status of all procured assets. It facilitates the creation of a centralized and comprehensive asset inventory, enabling seamless tracking of each asset’s condition, location, and lifecycle stage over time. With AIAMS, institutions can make data-driven decisions for maintenance, replacements, and future purchases, ensuring optimal resource utilization and operational efficiency.
Key Features of AIAS
Key Features of AIAS
- Asset Identification
Asset Types and Categories
Asset Classification [HSN and Local]
- Asset Description
- Asset Purchase details
- Asset Inventory Creation
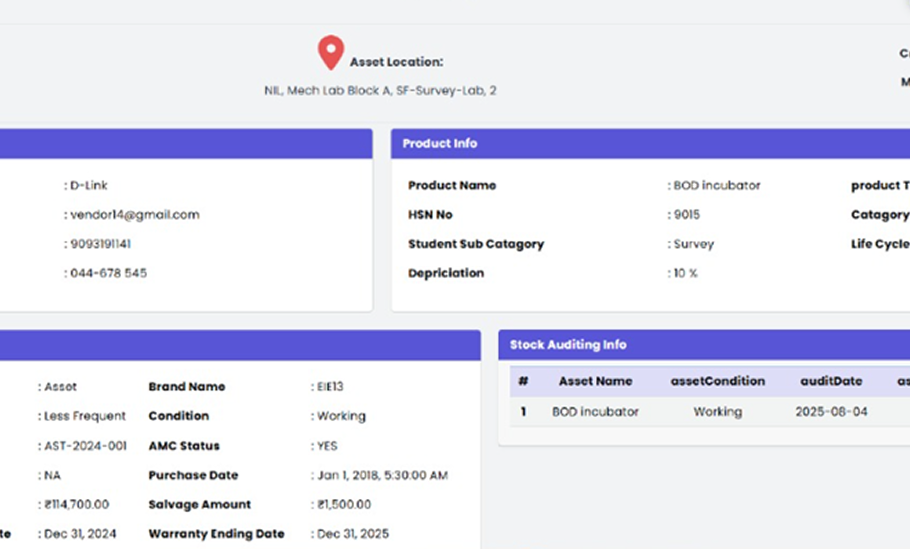
- Asset Location
- Asset Issue Tracking
- Asset Periodical Verification
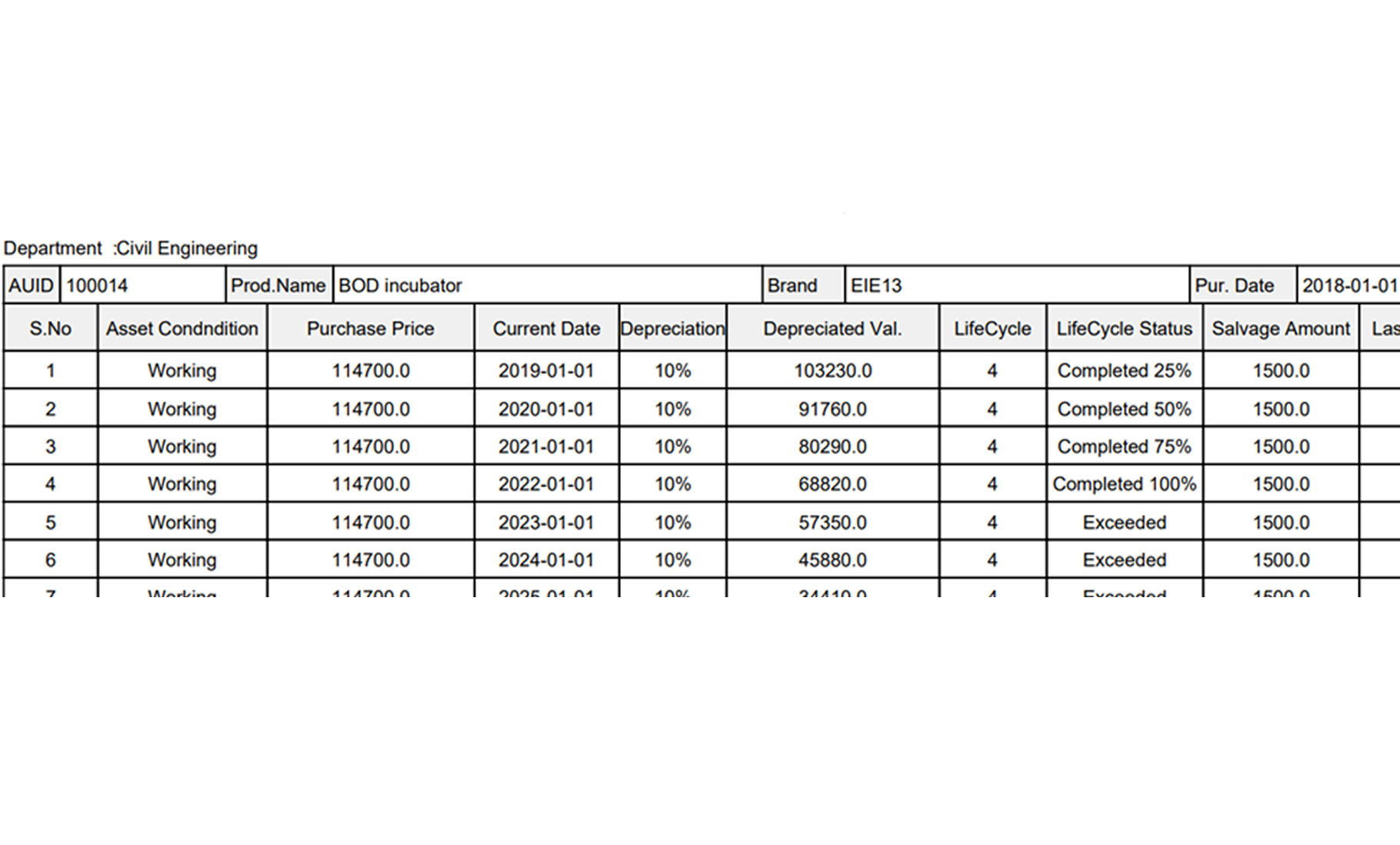
- Lifecycle and Depreciation Monitoring
- Asset Usage and Condition
- Warranty and AMC Status
- Audit and Reporting
- Purchase Planning